Way2go Card Login – How to Check Your Card Balance
If you’ve ever been handed a Way2Go card, you probably wondered how to log in, how to use it, and what makes it different...
www.twc.texas.gov Login – Everything You Need to Know
If you’ve landed here, chances are you’re trying to figure out the ins and outs of the www.twc.texas.gov login process. Maybe you’re applying for...
Texas Workforce Login – Access to Unemployment Services
Ever wondered how to handle your job search, unemployment benefits, or employer reporting in Texas? It all starts with the Texas Workforce Login. Whether...
True Link Card Holder Login – How to Access Your Account Online
If you’ve ever found yourself scratching your head over how to use the True Link card holder login, trust me, you’re not alone. A...
Cincinnati Insurance Agent Login – Access to Insurance Agent Portal
Cincinnati Insurance Agent Login isn’t just a random online tool, it’s a lifeline if you’re handling multiple policies, claims, or clients. Whether you’re an...
www.republicservices.com – Bill Pay
www.republicservices.com - bill pay has made life much easier for its users. Juggling multiple bills every month can feel like a never-ending game of...
Kitsap Credit Union Login – How to Secure Online Banking Access
The kitsap credit union login portal became a daily companion when it comes to managing your money locally. If you’re like me, juggling bills,...
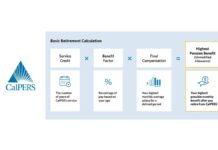
Calpers Retirement Calculator – How to Use
When I first stumbled across the CalPERS Retirement Calculator, I’ll be honest I felt a bit intimidated. It sounded like something complicated, only for...
Andrews Federal Credit Union Login – Online Step-by-Step
Perhaps you value convenience when it comes to handling your money. That’s why using the Andrews Federal Credit Union login feature makes keeping track...
Bass Pro Shop Credit Card Login – Log in to Access Your Account
If you’re anything like me, you probably get a little spark of joy at the mere mention of outdoor gear. That’s where Bass Pro...